[ad_1]
Rising fear of supply deficit has led oil prices to shed the inertia seen in the first half after Saudi Arabia and Russia extended voluntary production cuts until end of the year and US oil output projected to hit lowest since May. Mounting optimism over demand recovery in China, the world’s largest oil consumer, only added to the rally.
The spurt in oil prices is unlikely to burn a hole in wallets of motorists. The government is unlikely to announce an increase in pump prices by public sector fuel retailers, which dominate 90% of the market and have pricing freedom on paper.
Raising fuel prices at this juncture will stoke inflation when it is showing signs of easing and give the Opposition an opportunity to target the ruling party in poll states. This will leave fuel retailers holding the can once again. The freeze on prices through 2022-23 had resulted in a combined loss of Rs 21,000 crore for IOC, BPCL and HPCL in the first half as under-recovery on petrol and diesel hit Rs 12-14/litre at one point.
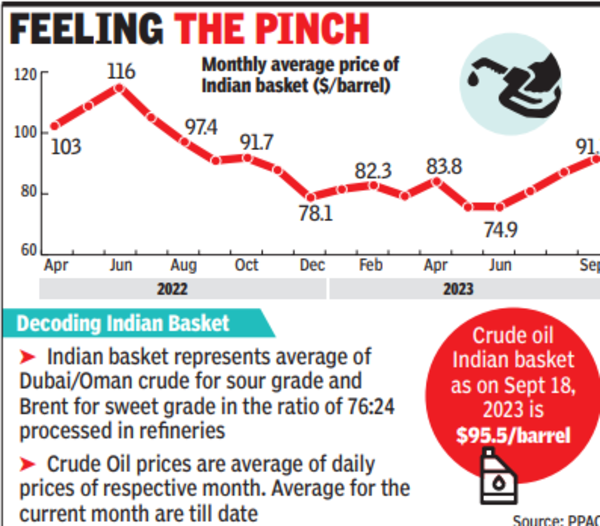
The prices remain frozen since May 2022 when the Centre last reduced excise duty and oil prices hovered around $85 per barrel. Rates were not reduced even after oil stayed below $80 in recent months. As reported by TOI earlier, this was done to allow retailers to recoup past losses and build a buffer for future. With hefty first quarter profits in their kitty, the Centre is sure to call in the support, turning petrol and diesel sales unprofitable once again. The falling rupee will make the pinch harder.
The impact on the economy will, however, be different as India depends on imports to meet 80% of oil requirements. Costlier crude squeezes the government’s leg room for social welfare spending by inflating the import bill, which weakens the rupee by impacting the current account deficit (CAD). Higher oil prices will prolong inflationary fears and prompt RBI to continue with its pause on interest rates for longer, dashing hopes of cheaper EMIs.
“The pick-up in crude prices, if sustained, can show up in headline consumer inflation print via direct (higher pump prices) and indirect effects (rising production and transportation costs),” said D K Joshi, chief economist at Crisil. “Fuel and core inflation have so far been benign below 5% and the inflation spike in July and August was entirely food-led,” said Joshi.
[ad_2]
Source link










More Stories
India’S Growth Forecast: S&P ups India’s FY’24 growth forecast to 6.4% on robust domestic momentum
India to remain fastest-growing major economy, but demand uneven: Poll
Jack Ma: Jack Ma gets back into business with ‘Ma’s Kitchen Food’